Application security vulnerabilities in legacy systems arise due to outdated software, unpatched security flaws, and lack of modern security measures. These issues can lead to data breaches, unauthorized access, and increased risk for organizations.
Legacy systems often serve critical business functions but pose significant security risks. Many organizations struggle to maintain these systems, which may run on obsolete technologies. The absence of regular updates and patches leaves them vulnerable to cyber threats. Attackers often exploit these weaknesses, targeting sensitive data and compromising system integrity.
Organizations must prioritize assessing their legacy systems, implementing security measures, and considering modernization options. By addressing vulnerabilities proactively, businesses can enhance their security posture and protect vital information from potential breaches.
Legacy Systems And Application Security
Legacy systems are outdated technologies still in use today. They often hold critical business functions. However, these systems pose significant application security vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks is essential for organizations.
The Age Of Legacy Systems
Many organizations rely on legacy systems. These systems can be decades old. They often run on outdated software and hardware. Common examples include:
- Mainframe systems
- Old database systems
- Custom-built applications
Legacy systems may seem stable. They often lack modern features. This stability can lead to complacency in security measures.
Security Concerns In Outdated Technologies
Legacy systems present various security concerns:
| Vulnerability Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Unpatched Software | Outdated software lacks important security updates. |
| Weak Authentication | Old systems often use weak password policies. |
| Data Exposure | Legacy systems may not encrypt sensitive data. |
| Limited Support | Vendors may no longer support these systems. |
Organizations face risks with legacy systems. Cyber attackers often exploit outdated technology. Regular audits and updates are crucial.
Addressing these vulnerabilities can prevent data breaches. Here are steps to enhance security:
- Conduct regular security assessments.
- Implement strong authentication methods.
- Encrypt sensitive data.
- Replace outdated systems when possible.
Managing legacy systems requires vigilance. Security teams must prioritize updates and training. The goal is to protect sensitive information effectively.

Credit: www.solix.com
Common Vulnerabilities In Legacy Applications
Legacy applications often face many security issues. These vulnerabilities arise from outdated technologies and lack of updates. Understanding these common vulnerabilities helps protect data and systems.
Unpatched Software Issues
Unpatched software is a major concern for legacy applications. Many organizations neglect updates, leaving systems exposed. Below are key reasons why unpatched software is risky:
- Security Flaws: Older software may have known vulnerabilities.
- Increased Attacks: Hackers target unpatched systems frequently.
- Compliance Risks: Failing to update may violate industry regulations.
Regular updates can help mitigate these risks. Organizations should prioritize patch management to protect their legacy systems.
Deprecated Functions And Protocols
Using deprecated functions and protocols poses significant threats. These outdated methods lack support and security fixes. Here are some common deprecated items:
| Deprecated Function/Protocol | Risk Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| SSL 2.0/3.0 | High | Upgrade to TLS 1.2 or higher |
| Java Applets | Medium | Transition to HTML5 or JavaScript |
| ActiveX Controls | High | Avoid usage, seek alternatives |
Outdated functions and protocols can lead to data breaches. Regular reviews and updates are essential for maintaining security.
The Impact Of Neglected Updates
The impact of neglected updates in legacy systems can be severe. Outdated software increases the risk of security breaches. Organizations often overlook the importance of regular updates. This negligence can lead to serious vulnerabilities.
Risks Of Running Obsolete Software
Legacy systems often run on obsolete software. This creates several risks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Hackers exploit known flaws.
- Compliance Issues: Outdated systems may not meet regulations.
- Data Loss: Unpatched software can result in data breaches.
- Increased Costs: Fixing issues in old software can be expensive.
Companies face real dangers from obsolete software. These risks can lead to:
- Loss of customer trust.
- Financial losses.
- Legal troubles.
Challenges With Patch Management
Patch management for legacy systems poses unique challenges:
- Resource Constraints: Limited staff may struggle to manage updates.
- Compatibility Issues: New patches may not work with older systems.
- Testing Delays: Time-consuming testing can slow down updates.
- Lack of Documentation: Old systems often lack clear update paths.
These challenges make it hard to maintain security. Organizations must prioritize patch management. Regular updates protect against vulnerabilities.
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Resource Constraints | Delays in applying necessary patches |
| Compatibility Issues | Potential for system failures |
| Testing Delays | Increased risk during the update process |
| Lack of Documentation | Confusion during patch management |
Threat Actors And Legacy Systems
Legacy systems are often old and outdated. They hold vital data but lack modern security. Threat actors target these systems due to their vulnerabilities. Understanding these attackers helps organizations protect themselves.
Targeting The Weak Links
Threat actors see legacy systems as easy targets. Here are some reasons why:
- Outdated Software: Many legacy systems run old software. This software lacks security updates.
- Weak Authentication: Some systems have poor password controls. This makes it easy to gain access.
- Limited Monitoring: Legacy systems often lack real-time monitoring. Attackers can operate undetected.
These weak points attract different types of hackers:
| Type of Hacker | Motivation |
|---|---|
| Cybercriminals | Financial gain through theft or ransom. |
| Hacktivists | Political motives or social justice. |
| State-sponsored | Espionage and data theft. |
Exploitation Techniques Used By Hackers
Hackers use various methods to exploit legacy systems. Some common techniques include:
- SQL Injection: Attackers insert malicious SQL code. This compromises databases.
- Phishing: Users receive fake emails. They can unknowingly provide sensitive information.
- Malware: Hackers deploy harmful software. This can take control of the system.
Organizations must stay informed about these techniques. Regular training can help employees recognize threats.
Compliance And Regulatory Hurdles
Legacy systems often struggle with compliance and regulatory standards. These systems may not meet modern security requirements. This gap exposes organizations to risks. Compliance is critical for protecting sensitive data.
Meeting Modern Standards
Organizations must align legacy systems with current standards. Here are key compliance frameworks:
- GDPR: Protects personal data in the EU.
- HIPAA: Safeguards health information in the USA.
- PCI DSS: Ensures secure payment processing.
Legacy systems often lack necessary features for these standards. They may not support encryption or secure access controls. Organizations must assess their systems for compliance gaps.
Penalties For Non-compliance
Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties. Here are some potential repercussions:
| Compliance Standard | Penalty Type | Potential Fine |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Financial penalties | Up to €20 million or 4% of annual revenue |
| HIPAA | Civil and criminal penalties | Up to $1.5 million per violation |
| PCI DSS | Fines and increased transaction fees | Up to $500,000 per incident |
Organizations face loss of trust and reputation. Customers may avoid businesses that fail to comply. Protecting sensitive data is crucial for maintaining customer relationships.
Balancing Functionality And Security
Legacy systems provide essential functions but can face security risks. Balancing functionality and security is crucial. Organizations often prioritize operations. This approach can expose them to vulnerabilities. Understanding this balance helps protect data and maintain performance.
Maintaining Operational Continuity
Operational continuity is vital for businesses. Legacy systems often support critical processes. Disruptions can lead to financial losses and customer dissatisfaction.
- Identify essential functions.
- Evaluate risks associated with legacy systems.
- Implement backup processes to ensure smooth operations.
Consider these strategies to maintain continuity:
- Regularly update software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor system performance continuously.
- Train staff on security awareness.
Implementing Security Best Practices
Security best practices can enhance legacy system safety. They help minimize risks while maintaining functionality. Here are key practices to adopt:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Audits | Conduct audits to identify vulnerabilities. |
| Access Controls | Limit access to sensitive data and systems. |
| Data Encryption | Encrypt data to protect it from unauthorized access. |
| Security Patches | Apply security patches promptly to fix vulnerabilities. |
Implement these practices to protect legacy systems. Regular updates and monitoring improve security without sacrificing performance.
Upgrading Legacy Systems
Upgrading legacy systems is vital for security and efficiency. Old systems often have application security vulnerabilities. These can lead to data breaches and loss of trust. Modernizing these systems helps protect sensitive information.
Strategies For Secure Migration
Secure migration of legacy systems requires careful planning. Here are some effective strategies:
- Assess Current Systems: Identify vulnerabilities in existing systems.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select modern tools that meet security standards.
- Implement Incremental Upgrades: Upgrade in stages to minimize risks.
- Data Backup: Always back up data before migration.
- Test Thoroughly: Conduct security tests on new systems.
Cost-benefit Analysis Of System Upgrades
Upgrading systems involves costs but provides significant benefits. Below is a simple cost-benefit analysis:
| Cost Factors | Benefit Factors |
|---|---|
| Initial investment in new technology | Enhanced security features |
| Training for employees | Increased efficiency and productivity |
| Downtime during migration | Reduced risk of data breaches |
| Maintenance costs | Long-term cost savings |
Balancing costs and benefits helps organizations make informed decisions. Investing in upgrades may seem high but protects against larger losses.

Credit: insart.com
Case Studies And Lessons Learned
Understanding application security vulnerabilities in legacy systems is crucial. Analyzing past incidents offers valuable lessons. Case studies reveal patterns in breaches and successes. These insights help organizations strengthen their security measures.
Historical Breaches
Many legacy systems have faced severe breaches. Here are some notable examples:
| Year | Company | Impact | Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Target | 40 million credit cards stolen | Weak third-party vendor security |
| 2017 | Equifax | 147 million records compromised | Unpatched software vulnerability |
| 2020 | Marriott | 500 million guest records exposed | Legacy database security flaws |
These breaches highlight the risks of outdated systems. Organizations must address security vulnerabilities to protect sensitive data. Ignoring these risks can lead to massive financial losses and reputational damage.
Success Stories In Modernizing Security Posture
Some companies have successfully modernized their security. Here are a few success stories:
- Company A: Upgraded legacy software to a cloud-based solution. This change improved security and reduced downtime.
- Company B: Implemented regular security audits. These audits identified weaknesses and allowed for timely updates.
- Company C: Trained employees on security best practices. This training reduced human error and phishing attacks.
Lessons learned from these successes include:
- Invest in modern technology to enhance security.
- Conduct regular security assessments to identify risks.
- Provide ongoing employee training on security awareness.
These steps can help organizations strengthen their defenses against potential threats.
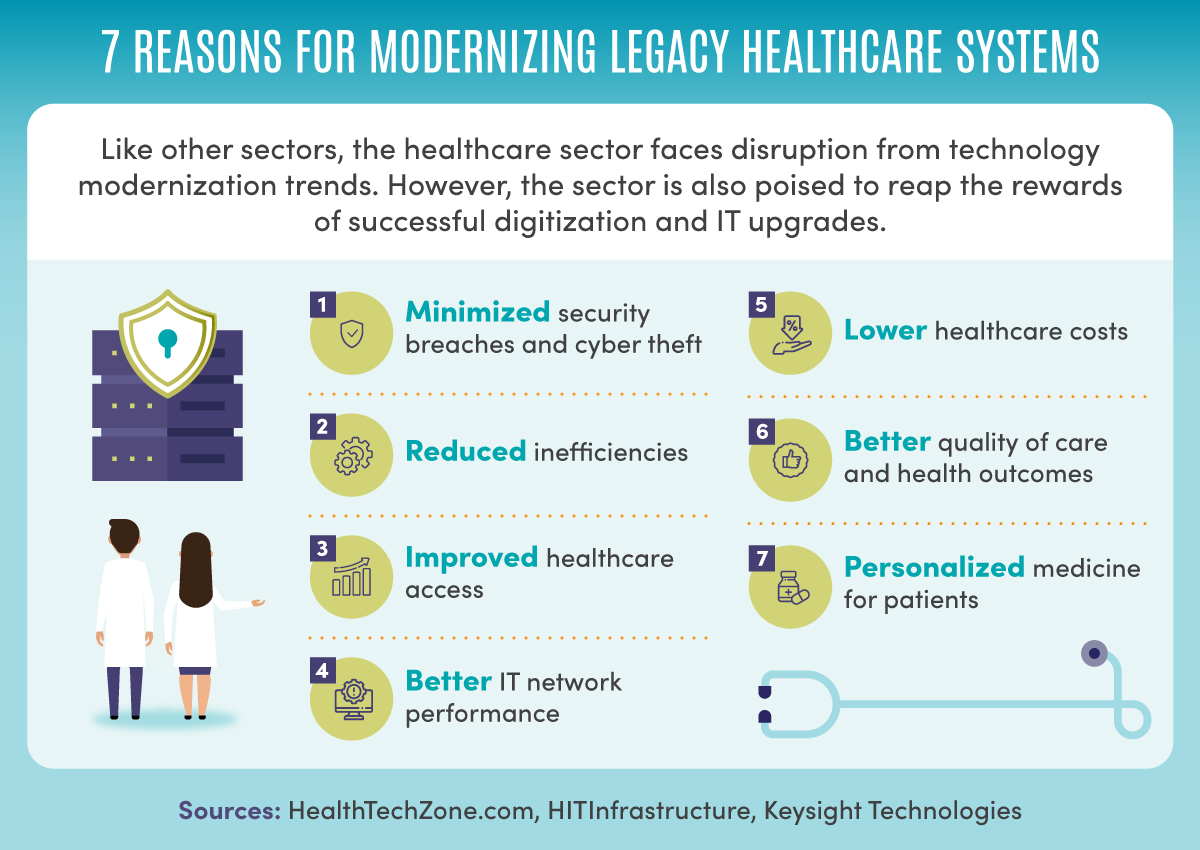
Credit: online.maryville.edu
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Legacy Systems In Application Security?
Legacy systems are outdated software or hardware still in use. They often lack modern security features, making them vulnerable to attacks. Organizations may struggle to upgrade these systems due to costs or compatibility issues. As a result, they become prime targets for cyber threats.
Why Are Legacy Systems Vulnerable To Attacks?
Legacy systems are vulnerable due to outdated security protocols and unpatched software. Many lack regular updates, leaving known vulnerabilities exposed. Additionally, these systems often integrate with newer technologies, creating security gaps. Cybercriminals exploit these weaknesses, posing significant risks to sensitive data and infrastructure.
How Can Organizations Secure Legacy Systems?
Organizations can secure legacy systems by implementing layered security measures. Regular audits and assessments help identify vulnerabilities. Applying patches and updates, where possible, is crucial. Additionally, segmenting legacy systems from the main network can reduce exposure to threats. Training staff on security best practices is equally important.
What Are Common Vulnerabilities In Legacy Systems?
Common vulnerabilities in legacy systems include unpatched software, weak authentication, and insecure configurations. These systems often use outdated encryption methods, making data interception easier. Poor documentation and insufficient monitoring can further complicate security efforts. Recognizing and addressing these vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining security.
Conclusion
Addressing application security vulnerabilities in legacy systems is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data. Organizations must prioritize regular assessments and updates to mitigate risks. Implementing modern security practices can significantly enhance protection. By staying vigilant and proactive, businesses can better defend against potential threats and ensure a more secure digital environment for their operations.




Leave a Reply