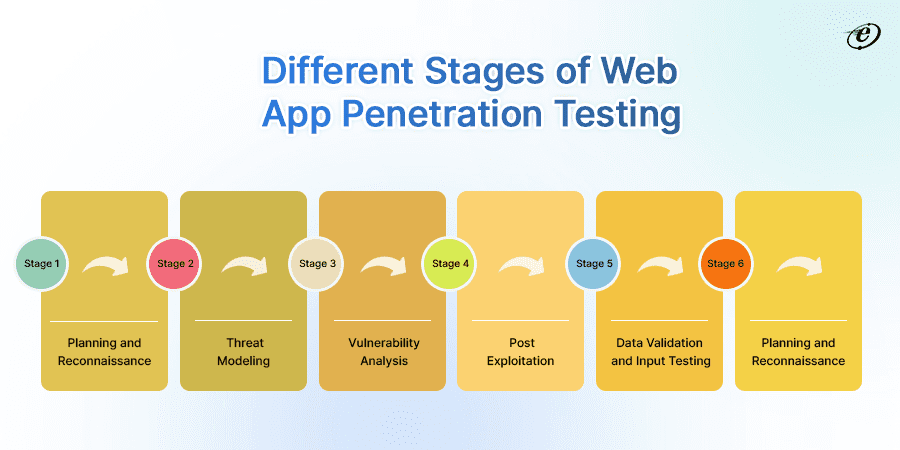
To conduct a web application penetration test, follow these steps: define the scope, gather information, identify vulnerabilities, exploit weaknesses, and report findings. Each step is crucial for assessing security and mitigating risks.
Web application penetration testing is vital for identifying security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. As online threats increase, organizations must ensure their applications are secure. This testing simulates real-world attacks, helping to uncover weaknesses that could lead to data breaches.
By understanding the security posture of a web application, businesses can prioritize fixes and safeguard sensitive information. A systematic approach to penetration testing not only enhances security but also builds trust with users. This guide will walk you through each step of the process, ensuring a thorough and effective assessment of your web application’s defenses.
Introduction To Web Application Penetration Testing
Web Application Penetration Testing is a vital security practice. It helps identify vulnerabilities in web applications. Companies use this testing to protect sensitive data. Attackers often target web applications to exploit weaknesses.
This testing simulates real-world attacks. It evaluates how well an application stands against threats. By conducting penetration tests, organizations can improve their security posture.
Importance In The Cybersecurity Landscape
Web applications are essential for business operations. They store valuable information like user data and financial records. Cybersecurity threats are on the rise, making penetration testing crucial.
Here are some key reasons why penetration testing is important:
- Identifies security weaknesses before attackers do.
- Ensures compliance with industry regulations.
- Builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
- Reduces potential financial losses from breaches.
Key Objectives Of Penetration Testing
The primary goals of penetration testing include:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Find security gaps in the application.
- Assess Risk: Evaluate the impact of potential breaches.
- Validate Security Controls: Check if existing security measures are effective.
- Enhance Security Awareness: Educate the team about security risks.
These objectives help organizations strengthen their defenses. Effective penetration testing leads to better security strategies.
Credit: eluminoustechnologies.com
Essential Tools For Penetration Testers
Penetration testing requires effective tools for successful outcomes. These tools help identify security weaknesses in web applications. Choosing the right tools can make a significant difference. Below are key aspects of essential tools for penetration testers.
Choosing The Right Software
Selecting software is crucial for effective penetration testing. Here are some popular options:
- Burp Suite: A powerful web application security testing tool.
- OWASP ZAP: An open-source tool for finding security vulnerabilities.
- Nessus: A comprehensive vulnerability scanning tool.
- Metasploit: A framework for developing and executing exploit code.
Each software has unique features. Consider the following factors:
- User Interface: Ensure it is user-friendly.
- Community Support: A strong community can provide assistance.
- Cost: Balance between free and paid options.
- Compatibility: Check if it works with your systems.
Hardware Requirements For Testing
Good hardware is essential for running penetration tests effectively. Here are the basic requirements:
| Component | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| CPU: | Quad-core processor |
| RAM: | 8 GB (16 GB recommended) |
| Storage: | 256 GB SSD or more |
| Network: | Reliable internet connection |
Investing in quality hardware enhances testing efficiency. Faster processing speeds lead to quicker results. Ensure hardware meets or exceeds these requirements.
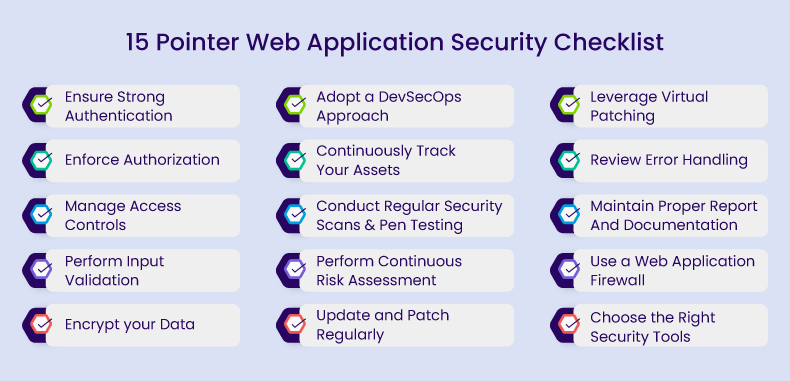
Preparation And Planning
Effective preparation is crucial for a successful web application penetration test. This phase lays the groundwork for your testing process. It involves defining the scope, understanding legal requirements, and obtaining necessary permissions. A well-planned test minimizes risks and ensures comprehensive coverage.
Scoping The Web Application
Scoping defines what parts of the application you will test. Clear scoping helps focus your efforts. Here are key elements to consider:
- Identify Targets: Specify which applications or services to test.
- Define Boundaries: Determine what is in-scope and out-of-scope.
- Set Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve.
Consider using a table to clarify your scope:
| Scope Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Name | Name of the web application. |
| IP Addresses | List of relevant IP addresses. |
| Testing Methods | Manual testing, automated scanning, etc. |
Legal Considerations And Permissions
Legal aspects are vital. Ensure compliance with laws and regulations. Follow these steps:
- Obtain Written Permission: Get explicit consent from the application owner.
- Review Legal Guidelines: Understand local laws about penetration testing.
- Sign an NDA: Protect sensitive information through a Non-Disclosure Agreement.
Failure to address these legalities can lead to serious consequences. Always prioritize ethical hacking standards. This ensures a responsible and lawful testing process.
Credit: www.indusface.com
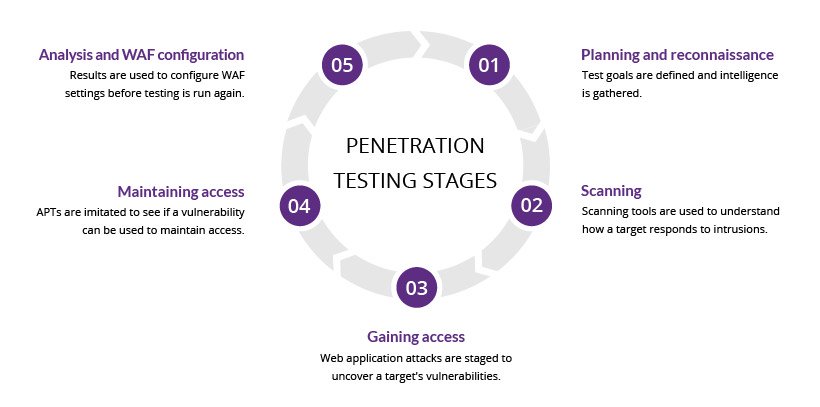
Information Gathering And Reconnaissance
Information gathering and reconnaissance is the first step in a web application penetration test. This phase focuses on collecting data about the target. The goal is to identify potential vulnerabilities. Effective reconnaissance helps in planning the attack strategy.
Techniques For Effective Recon
Several techniques can enhance your reconnaissance efforts:
- Google Dorking: Use specific search queries to find sensitive data.
- WHOIS Lookup: Gather domain registration details.
- DNS Enumeration: Discover subdomains and IP addresses.
- Social Engineering: Gather information from employees or users.
- Port Scanning: Identify open ports on the server.
Automated Vs Manual Information Collection
Both automated and manual methods are vital for effective testing.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Automated |
|
|
| Manual |
|
|
Combining both methods yields the best results. Use automated tools for initial data collection. Then apply manual techniques for detailed insights. This approach maximizes your chances of uncovering vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Assessment
The vulnerability assessment is a crucial part of web application penetration testing. It helps identify weaknesses in the system. Knowing these weaknesses allows developers to fix them before attackers can exploit them.
Identifying Potential Weaknesses
Start by gathering information about the web application. This includes:
- Application architecture
- Third-party components
- Security policies
Next, examine the following areas:
- Input Validation: Check how the application handles user input.
- Authentication: Review login mechanisms and password policies.
- Session Management: Analyze how sessions are maintained and expired.
- Access Control: Look for unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Document all findings. This will help in the testing process later on.
Using Vulnerability Scanners
Vulnerability scanners are essential tools in this phase. They automate the process of finding weaknesses. Here are some popular scanners:
| Scanner Name | Key Features |
|---|---|
| OWASP ZAP | Open-source, user-friendly, detects a wide range of vulnerabilities. |
| Nessus | Comprehensive scanning, customizable, extensive reporting. |
| Burp Suite | Integrated tools, manual and automated testing options. |
Run the scanner against the web application. Analyze the results carefully. Focus on high-risk vulnerabilities first. Prioritize fixing them to enhance security.
Exploitation Phase
The Exploitation Phase is crucial in a web application penetration test. Here, testers actively exploit identified vulnerabilities. This step shows how attackers might gain unauthorized access. Understanding this helps strengthen security measures.
Exploiting Identified Vulnerabilities
In this step, testers use tools and techniques to exploit weaknesses. The goal is to see how deep an attacker can go into the system.
- SQL Injection – Inject malicious SQL code to manipulate the database.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) – Insert scripts into web pages viewed by users.
- Command Injection – Execute system commands on the server.
Tools often used include:
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Burp Suite | Web application testing |
| OWASP ZAP | Finding security vulnerabilities |
| Metasploit | Exploitation framework |
Keep track of all exploited vulnerabilities. Document the methods used and the results obtained. This information is vital for the next steps.
Maintaining Access And Pivoting
After exploiting vulnerabilities, maintaining access is key. Testers seek to establish a foothold in the system.
- Backdoors – Install hidden access points for future use.
- Credential Harvesting – Collect usernames and passwords.
- Pivoting – Move laterally to other systems in the network.
Techniques for maintaining access include:
- Using persistent scripts.
- Creating new user accounts with admin privileges.
- Exploiting trust relationships between applications.
Documentation remains essential. Record every step taken to maintain access. This information aids in understanding potential risks.
Post-exploitation Activities
Post-exploitation activities are crucial in a web application penetration test. They help testers understand vulnerabilities and gather valuable data. This phase involves two main tasks: data analysis and clearing tracks.
Data Analysis And Extraction
Data analysis and extraction involve reviewing collected data for sensitive information. This step helps in understanding how deep the breach goes.
- Identify sensitive data: Look for personal information, passwords, and financial data.
- Document findings: Keep a record of discovered vulnerabilities and data types.
- Extract data: Use tools to pull sensitive information for further analysis.
Here is a simple table to illustrate common data types:
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Addresses | Contact information of users. |
| Usernames | Identifies users in the system. |
| Password Hashes | Encrypted user passwords. |
| Credit Card Info | Financial data of users. |
Covering Tracks And Clearing Logs
Covering tracks ensures that the exploitation process remains undetected. Clearing logs prevents detection by system administrators.
- Delete access logs: Remove records of unauthorized access.
- Modify timestamps: Change logs to hide the timing of activities.
- Use stealth techniques: Employ tools to avoid detection.
Here are some common tools for covering tracks:
- Log Cleaner
- Access Mask
- Stealthy
Always remember, ethical considerations are vital in post-exploitation activities. Respect user privacy and handle data responsibly.

Credit: medium.com
Reporting And Communication
Effective reporting and communication are key after a web application penetration test. Clear communication helps stakeholders understand the risks. It also aids in prioritizing actions based on findings. Let’s explore how to document findings and provide actionable recommendations.
Documenting Findings
Documenting findings is essential for clarity. Use a structured format. Include these elements:
- Executive Summary: Brief overview of the test results.
- Scope: Details of the tested application.
- Methodology: Testing methods used during the assessment.
- Findings: Detailed list of vulnerabilities discovered.
Organize findings in a table for easy reading:
| Vulnerability | Severity | Description | URL |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | High | Allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands. | http://example.com/vulnerable |
| Cross-Site Scripting | Medium | Enables attackers to inject scripts into pages. | http://example.com/xss |
Providing Actionable Recommendations
Recommendations should be clear and actionable. Use specific language. This helps teams understand what steps to take next.
- Prioritize Issues: Focus on high-severity vulnerabilities first.
- Assign Responsibilities: Identify who will address each issue.
- Provide Solutions: Suggest fixes for each vulnerability.
- Offer Resources: Share links to guides or tools for remediation.
For example, for SQL Injection:
- Use prepared statements to prevent injection.
- Validate and sanitize user inputs.
Communicate regularly with the development team. Discuss the findings and recommendations. This ensures everyone is on the same page. Clear communication speeds up remediation efforts.
Remediation And Retesting
After identifying vulnerabilities, it’s crucial to address them. Effective remediation minimizes risks. Retesting ensures that fixes are successful.
Guiding The Remediation Process
Follow these steps to guide the remediation process:
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on severity and impact.
- Develop a remediation plan with clear timelines.
- Assign tasks to appropriate team members.
- Implement fixes according to the plan.
Use a table to track progress:
| Vulnerability | Severity | Status | Assigned To |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | High | In Progress | Team A |
| Cross-Site Scripting | Medium | Not Started | Team B |
Verifying Security Enhancements
Verification ensures that all changes are effective. Follow these steps:
- Conduct retesting on fixed vulnerabilities.
- Test new features for any introduced vulnerabilities.
- Review security policies to ensure they align with updates.
- Document results for future reference.
Use automated tools for efficient verification. They quickly identify remaining vulnerabilities.
Regular reviews maintain security integrity. Schedule periodic assessments to stay secure.
Staying Updated With Web Security Trends
Web security evolves rapidly. New threats emerge daily. Staying informed is crucial for effective penetration testing. Use reliable sources to gain knowledge. This section covers how to keep your skills sharp.
Continuous Learning And Skill Development
Learning never stops in the field of web security. Here are effective ways to enhance your skills:
- Take online courses on platforms like Coursera or Udemy.
- Read books focused on web application security.
- Follow blogs from industry experts.
- Subscribe to relevant podcasts.
Hands-on practice is essential. Use labs like:
| Lab Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Hack The Box | Practice penetration testing in a safe environment. |
| OWASP Juice Shop | A vulnerable web app for testing security skills. |
Stay updated with certifications. Consider:
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP)
Participating In The Security Community
Engaging with the security community provides insights and support. Connect with others through:
- Forums like Reddit and Stack Overflow.
- Local meetups and conferences.
- Social media groups focused on cybersecurity.
Contributing to open-source projects boosts your profile. Share your knowledge and learn from others. Collaboration strengthens skills and community ties.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Web Application Penetration Testing?
Web application penetration testing is a simulated cyber attack. It identifies vulnerabilities in web applications. Testers use various techniques to exploit weaknesses. This helps organizations understand their security posture and prioritize fixes. Ultimately, it enhances the overall security of the application.
Why Is Penetration Testing Important For Web Apps?
Penetration testing is crucial for identifying security gaps. It protects sensitive data and builds customer trust. Regular testing ensures compliance with industry standards. It also helps organizations stay ahead of potential threats. Ultimately, it reduces the risk of data breaches.
How Often Should I Conduct Penetration Tests?
Organizations should conduct penetration tests at least annually. However, more frequent testing may be needed after major updates. Regular tests help identify new vulnerabilities. They also ensure existing security measures remain effective. Continuous testing is vital in today’s evolving threat landscape.
What Tools Are Used In Penetration Testing?
Common tools include Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and Nmap. These tools help identify vulnerabilities, automate tasks, and simulate attacks. Each tool has unique features that cater to different testing needs. Utilizing a combination of tools enhances the testing process. The right tools boost efficiency and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Conducting a web application penetration test is essential for security. Following the outlined steps ensures thorough evaluation and risk mitigation. Regular testing helps identify vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. Stay proactive in your security measures. This will protect your data and build user trust in your web applications.



Leave a Reply