Encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access. It ensures that information remains confidential and secure, even if intercepted.
Understanding the Importance of Encryption:In today’s digital landscape, data breaches and cyber threats are rampant. Organizations and individuals alike face the risk of exposing sensitive information. Encryption plays a vital role in safeguarding this data, making it unreadable to unauthorized users. It transforms plain text into coded information, requiring a key for decryption.
This process not only protects personal data but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders. With the increasing reliance on digital communications, understanding the importance of encryption is essential for maintaining privacy and security. Implementing robust encryption practices can significantly reduce the risk of data theft and enhance overall information security.

Credit: fastercapital.com
The Rise Of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are increasing every day. Hackers target individuals and businesses. They aim to steal sensitive information. This creates a dire need for strong security measures.
The Digital Age And Its Risks
The digital age offers many benefits. We can connect globally and share information easily. Yet, it also brings risks:
- Data Theft: Hackers steal personal and financial data.
- Identity Fraud: Criminals impersonate others online.
- Malware Attacks: Harmful software disrupts systems.
- Ransomware: Hackers lock data and demand payment.
Every device connected to the internet is at risk. Businesses must protect their data. Individuals should also secure personal information.
Recent Data Breaches And Lessons Learned
Data breaches happen frequently. They expose millions of records. Some notable breaches include:
| Company | Year | Records Exposed |
|---|---|---|
| Yahoo | 2013 | 3 billion |
| 2019 | 540 million | |
| Equifax | 2017 | 147 million |
Each breach teaches important lessons:
- Always use strong passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Regularly update software.
- Educate employees about security.
These steps can prevent future breaches. Understanding risks helps everyone stay safe.

Credit: www.scaler.com
Fundamentals Of Encryption
Encryption is essential for protecting sensitive information. It transforms data into a secure format. Only authorized users can access or read this information.
What Is Encryption?
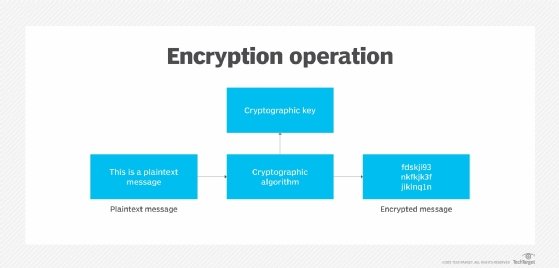
Encryption is the process of converting readable data into an unreadable format. This makes it difficult for unauthorized users to access the information. Here are some key points about encryption:
- It uses algorithms to secure data.
- Only those with a key can decrypt the data.
- Encryption protects data at rest and in transit.
Types Of Encryption Algorithms
Different algorithms serve various purposes in encryption. Below are the main types:
| Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetric Encryption | Uses the same key for encryption and decryption. | Fast and efficient for large amounts of data. |
| Asymmetric Encryption | Uses a pair of keys: public and private. | Secure data exchange over the internet. |
| Hashing | Converts data into a fixed-size string of characters. | Ensures data integrity. |
Understanding these types helps in choosing the right encryption method. Each has strengths and weaknesses. Knowing them aids in better information security.
Real-world Applications
Encryption plays a critical role in modern information security. Its applications protect sensitive data in various settings. Below are key areas where encryption is vital.
Protecting Personal Data
Personal data is everywhere. It includes names, addresses, and credit card numbers. Encryption keeps this data safe from hackers.
- Online Shopping: Secure transactions use encryption to protect payment details.
- Social Media: Messages and photos shared are encrypted to maintain privacy.
- Healthcare: Patient records are encrypted to ensure confidentiality.
Without encryption, personal data is at risk. Hackers can steal information easily. Encryption acts like a lock on your data.
Securing Business Communications
Businesses communicate sensitive information daily. Encryption safeguards these communications from unauthorized access.
- Email Security: Encrypted emails keep conversations private.
- File Sharing: Encrypted files ensure safe sharing of important documents.
- Virtual Meetings: Secure connections protect discussions from eavesdroppers.
| Application | Encryption Method |
|---|---|
| PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) | |
| File Sharing | AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) |
| Video Conferencing | SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) |
Encryption helps businesses protect their assets. It builds trust with clients. Secure communications lead to better relationships.
Key Benefits Of Encryption
Encryption plays a vital role in information security. It ensures that data remains protected from unauthorized access. Here are some key benefits of encryption that highlight its importance in safeguarding sensitive information.
Confidentiality Of Information
Encryption provides strong confidentiality for sensitive data. It transforms readable data into an unreadable format. Only authorized users can access the original information.
- Prevents unauthorized access to personal data.
- Protects financial information, like credit card details.
- Secures sensitive business documents from competitors.
By using encryption, organizations can ensure that their data remains private. This builds trust with customers and partners alike.
Integrity And Authentication
Encryption also enhances integrity and authentication. It verifies that data has not been altered or tampered with. This is crucial for maintaining accurate information.
- Data integrity ensures accuracy in transactions.
- Authentication confirms the identity of users.
- Protects against data breaches and fraud.
Using encryption helps organizations maintain a secure environment. This protects both their data and their reputation.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Protects data from unauthorized access. |
| Integrity | Ensures data remains accurate and unaltered. |
| Authentication | Verifies the identity of users accessing data. |
Encryption Techniques
Understanding different encryption techniques is vital for protecting data. These methods help secure information from unauthorized access. Two main types of encryption are symmetric and asymmetric. Each serves a unique purpose in information security.
Symmetric Vs Asymmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. This method is fast and efficient. However, it requires secure key management. If someone steals the key, they can access sensitive data.</p
Asymmetric encryption uses a pair of keys: a public key and a private key. The public key encrypts data, while the private key decrypts it. This method is more secure for transmitting data over the internet. It solves the key distribution problem found in symmetric encryption.</p
| Feature | Symmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Encryption |
|---|---|---|
| Key Type | Single key | Pair of keys |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Key Distribution | Challenging | Easy |
| Use Cases | File encryption | Secure communications |
Public Key Infrastructure (pki)
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) supports secure communication. It uses a combination of hardware, software, policies, and procedures. PKI manages digital certificates and public-key encryption.
- Authentication: Verifies identity of users and devices.
- Encryption: Secures data using public and private keys.
- Integrity: Ensures data has not been altered.
- Non-repudiation: Prevents denial of sending data.
PKI is crucial for online transactions and secure email. It builds trust in digital communications.
“`
Challenges In Implementing Encryption
Implementing encryption brings several challenges. These hurdles can impact efficiency and security. Understanding them is crucial for effective implementation.
Performance Overhead
Encryption can slow down system performance. The process requires extra computing power. Here are key points to consider:
- Encryption adds processing time.
- Decryption also consumes resources.
- Latency affects user experience.
For large data sets, this impact grows. Businesses must balance security and speed. Using efficient algorithms can help.
Key Management Issues
Managing encryption keys poses significant challenges. Poor key management can lead to data breaches. Consider these key management aspects:
- Key generation must be secure.
- Key storage should be protected.
- Key rotation is essential for security.
- Access to keys needs strict control.
Organizations must invest in proper tools. Training staff on key management is vital. Secure key management practices reduce risks.
Best Practices For Data Security
Data security is vital for protecting sensitive information. Implementing the right strategies ensures data remains safe from threats. Follow these best practices to enhance your encryption efforts and safeguard your data.
Encryption Protocol Selection
Choosing the right encryption protocol is crucial. Different protocols offer various levels of security. Below are popular encryption protocols:
| Protocol | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| AES | Advanced Encryption Standard | Data at rest and in transit |
| SSL/TLS | Secures web traffic | Online transactions |
| PGP | Pretty Good Privacy | Email encryption |
Select a protocol that fits your needs. Always prioritize strong encryption methods. Regularly update protocols to counter new threats.
Regular Security Audits
Conducting regular security audits is essential. Audits help identify weaknesses in your encryption practices. Follow these steps for effective audits:
- Assess current encryption methods.
- Check for compliance with industry standards.
- Test for vulnerabilities in data storage.
- Review access controls and permissions.
- Document findings and implement improvements.
Schedule audits at least once a year. Adjust your security measures based on audit results. Continuous monitoring keeps your data safe from emerging threats.
Credit: www.techtarget.com
The Future Of Encryption
Encryption plays a vital role in information security. Its future is shaped by advances in technology and emerging threats. Understanding these changes is crucial for protecting sensitive data.
Quantum Computing And Encryption
Quantum computing poses a significant challenge to traditional encryption methods. It can break many current encryption algorithms in seconds. This capability raises questions about data security.
Here are key points to consider:
- Quantum computers can solve complex problems much faster.
- Current encryption methods may become obsolete.
- New algorithms are needed to counter quantum threats.
Research is ongoing to develop quantum-resistant algorithms. These algorithms will safeguard data against quantum attacks. Here’s a comparison of traditional vs. quantum-resistant algorithms:
| Encryption Type | Vulnerability to Quantum Attacks |
|---|---|
| RSA | High |
| Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) | High |
| Post-Quantum Cryptography | Low |
Evolving Standards And Regulations
Encryption standards and regulations are constantly changing. Organizations must stay updated to ensure compliance. New laws often require stronger encryption measures.
Important regulations include:
- GDPR – Requires data protection and privacy for EU citizens.
- HIPAA – Mandates encryption for health information.
- PCI DSS – Protects payment card information.
Businesses must adapt to these evolving standards. Non-compliance can lead to hefty fines and data breaches. Regular audits and updates are essential for maintaining security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Encryption In Information Security?
Encryption is the process of converting data into a coded format. This ensures that only authorized users can access the information. By protecting sensitive data, encryption helps prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. It is a crucial element in maintaining confidentiality and integrity in information security.
Why Is Encryption Important For Data Protection?
Encryption is vital for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. It safeguards personal data, financial transactions, and confidential communications. By encrypting data, organizations can comply with regulations and build trust with customers. Ultimately, it enhances overall data security and mitigates potential risks.
How Does Encryption Work?
Encryption uses algorithms to transform readable data into an unreadable format. Only those with the correct decryption key can revert the data back to its original form. This process ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains inaccessible without the key.
Thus, encryption provides a robust layer of security.
What Are Common Types Of Encryption?
Common types of encryption include symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. In contrast, asymmetric encryption employs a pair of keys—public and private. Each type has its advantages and is used based on specific security needs.
Conclusion
Encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information. It safeguards personal data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Understanding its importance helps individuals and organizations strengthen their security measures. Embracing encryption not only protects privacy but also builds trust with customers.
Prioritize encryption for a safer digital landscape.




Leave a Reply