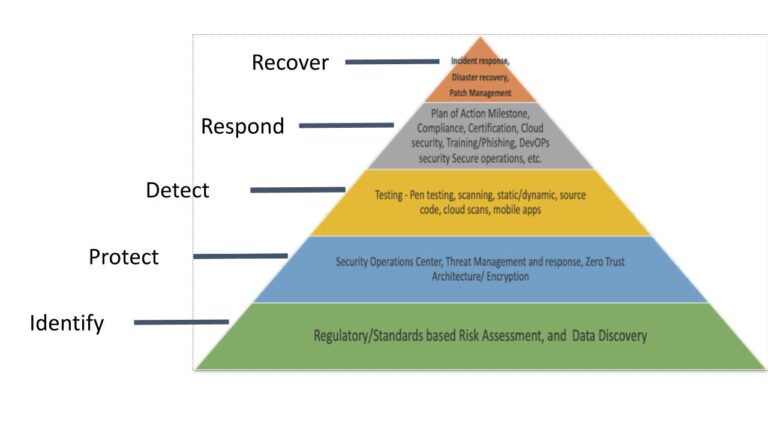
Penetration testing methodologies for small businesses include black-box, white-box, and gray-box testing. Each approach helps identify vulnerabilities based on different levels of information access.
Cybersecurity remains a top priority for small businesses facing increasing digital threats. Understanding penetration testing methodologies is essential for safeguarding sensitive data. Black-box testing simulates an external attack with no prior knowledge of the system. White-box testing offers full access to the internal workings of the system, allowing for a thorough assessment.
Gray-box testing combines both methods, providing insights from both perspectives. By implementing these methodologies, small businesses can detect vulnerabilities, improve their security posture, and protect against potential breaches, ensuring customer trust and compliance with regulations. Investing in penetration testing is vital for maintaining a resilient cybersecurity strategy.
The Need For Penetration Testing In Small Businesses
Small businesses face unique challenges in cybersecurity. Many believe they are too small to be targeted. This misconception can lead to severe vulnerabilities. Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated. Regular penetration testing helps identify weaknesses and secure systems.
Growing Cybersecurity Threats
Cyber attacks are increasing in frequency and severity. Small businesses often lack the resources to combat these threats. Here are some common threats:
- Phishing attacks – Deceptive emails trick employees.
- Ransomware – Malicious software locks data until a ransom is paid.
- Data breaches – Unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Insider threats – Employees misusing access for personal gain.
These threats can result in financial loss and damage to reputation.
Benefits Of Regular Security Assessments
Regular penetration testing offers numerous benefits for small businesses:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Identifying vulnerabilities | Tests reveal weaknesses in systems and applications. |
| Improving compliance | Helps meet industry regulations and standards. |
| Enhancing customer trust | Demonstrates commitment to protecting customer data. |
| Reducing financial loss | Prevents costly data breaches and system downtimes. |
Investing in penetration testing strengthens security posture. It protects valuable assets and builds customer confidence.
Key Concepts In Penetration Testing
Understanding penetration testing is crucial for small businesses. It helps identify security weaknesses. This section covers basic concepts that every business owner should know.
What Is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing is a method to evaluate a system’s security. It simulates real-world attacks. Security experts, known as pen testers, try to exploit vulnerabilities.
The goal is to find weak spots before attackers do. Businesses can then strengthen their defenses. This proactive approach saves time and money.
Types Of Penetration Tests
Different types of penetration tests exist to suit various needs:
| Type of Test | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Penetration Test | Focuses on network security and vulnerabilities. |
| Web Application Test | Targets web applications for security flaws. |
| Social Engineering Test | Tests human factors and employee awareness. |
| Physical Penetration Test | Assesses physical security measures. |
Each type of test serves a specific purpose. Choose the right type based on your needs. Here are some common methods:
- Black Box Testing: Testers have no prior knowledge of the system.
- White Box Testing: Testers have full access to the system.
- Gray Box Testing: Testers have limited knowledge of the system.
Understanding these key concepts prepares small businesses for effective security measures. Protect your assets with the right penetration testing approach.
Setting The Stage: Pre-testing Considerations
Before diving into penetration testing, small businesses must prepare. Proper preparation ensures effective testing and minimizes risks. Consider two main aspects: defining the scope and understanding legal implications.
Defining The Scope And Goals
Clearly outline what the penetration test will cover. This step focuses on:
- Target Systems: Identify which systems are in scope.
- Testing Type: Choose between black-box, white-box, or grey-box testing.
- Objectives: Define what you aim to achieve.
Set specific goals. This can include:
- Finding vulnerabilities.
- Testing security controls.
- Improving overall security posture.
Document the scope. Share it with all stakeholders. This ensures everyone understands the testing limits and goals.
Legal And Compliance Implications
Understanding legal implications is vital. Penetration testing can have legal consequences. Follow these guidelines:
- Contracts: Establish clear agreements with testing firms.
- Authorization: Obtain written permission for testing.
- Compliance Standards: Check if you meet industry regulations.
Common compliance standards include:
| Compliance Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| GDPR | Regulates data protection in the EU. |
| PCI DSS | Standards for card payment security. |
| HIPAA | Protects health information in the US. |
Always consult a legal expert. This ensures compliance with laws. Avoid potential penalties or lawsuits.
Common Penetration Testing Frameworks
Penetration testing frameworks help small businesses find security gaps. These frameworks guide testers in evaluating systems effectively. They ensure that tests are thorough and reliable. Here are two popular frameworks used in penetration testing.
Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual (osstmm)
The OSSTMM is a well-known framework. It provides a detailed approach to security testing. This methodology focuses on how to test security systems. Here are its main features:
- Comprehensive Guidelines: Covers various aspects of security.
- Structured Testing: Ensures systematic testing processes.
- Open Source: Free to use and modify.
OSSTMM helps businesses understand their security posture. It defines metrics for measuring security. This framework is suitable for small businesses that need clear and effective testing methods.
Information Systems Security Assessment Framework (issaf)
The ISSAF offers a structured approach to security assessments. This framework is designed for information systems. It helps businesses identify vulnerabilities and risks. Key aspects include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Step-by-Step Process | Guides testers through each phase of assessment. |
| Focus on Compliance | Ensures alignment with industry standards. |
| Risk Management | Helps prioritize risks effectively. |
ISSAF is ideal for small businesses aiming for compliance. It supports effective risk management and security assessment.
Phases Of Penetration Testing
Understanding the phases of penetration testing is crucial for small businesses. Each phase plays a vital role in identifying weaknesses. This structured approach helps protect sensitive data.
Reconnaissance And Intelligence Gathering
The first phase is reconnaissance. This involves collecting information about the target system. Attackers gather data to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Identify the network and IP addresses.
- Gather information about employees.
- Use social engineering techniques.
- Analyze the target’s online presence.
Tools like Nmap and Maltego are useful in this phase.
Scanning And Vulnerability Assessment
The second phase focuses on scanning. This helps pinpoint vulnerabilities in the system. Scanning tools analyze open ports and services.
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Nessus | Vulnerability scanning |
| OpenVAS | Network vulnerability scanning |
| Burp Suite | Web application scanning |
Vulnerabilities found here must be prioritized based on risk.
Exploitation
Exploitation is the third phase. Here, testers attempt to exploit identified vulnerabilities. This phase simulates real-world attacks.
- Gain access to systems.
- Steal sensitive data.
- Test the effectiveness of defenses.
It is essential to document all actions taken during this phase.
Post-exploitation And Reporting
The final phase is post-exploitation. This involves analyzing the impact of successful attacks. Testers create a detailed report.
- Summarize findings.
- Provide recommendations for mitigation.
- Highlight critical vulnerabilities.
Reports should be clear and actionable for business owners. This helps in strengthening security measures.

Credit: rfply.com
Tools Of The Trade
Small businesses need effective tools for penetration testing. These tools help identify and fix security issues. Understanding these tools is crucial for maintaining safety.
Networking Tools
Networking tools are essential for analyzing network traffic. They help discover vulnerabilities in your systems. Here are some popular networking tools:
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer. It captures and analyzes packets.
- Nmap: A network scanner. It discovers hosts and services.
- Tcpdump: A command-line packet analyzer. It captures traffic for detailed analysis.
These tools provide insights into network behavior. They help detect unauthorized access and potential threats.
Vulnerability Scanners
Vulnerability scanners automate the detection of security flaws. They scan systems and report potential weaknesses. Key vulnerability scanners include:
| Tool Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Nessus | A widely used scanner. It checks for known vulnerabilities. |
| OpenVAS | An open-source scanner. It offers comprehensive vulnerability assessments. |
| Qualys | A cloud-based scanner. It provides continuous monitoring and reporting. |
Using these scanners helps small businesses stay secure. Regular scans identify new vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
Exploitation Frameworks
Exploitation frameworks allow testers to simulate attacks. They help verify the effectiveness of security measures. Common exploitation frameworks include:
- Metasploit: A powerful framework for developing and executing exploits.
- Canvas: A commercial framework. It offers advanced exploitation capabilities.
- Core Impact: A versatile tool for penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
These frameworks provide real-world attack simulations. They help businesses understand their vulnerabilities better.
Best Practices For Effective Penetration Testing
Effective penetration testing helps small businesses identify security weaknesses. Following best practices ensures accurate results and better security measures. Here are the key practices to implement.
Continuous Learning And Skill Development
Cybersecurity is always changing. Regular training keeps skills sharp. Here are some strategies:
- Attend workshops and seminars.
- Take online courses on platforms like Coursera or Udemy.
- Read books and articles on the latest security trends.
Encourage team members to earn certifications. Popular ones include:
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| CEH | Certified Ethical Hacker |
| OSCP | Offensive Security Certified Professional |
| CISSP | Certified Information Systems Security Professional |
Regularly assess the team’s skills. Use real-world scenarios for practice.
Engaging With The Cybersecurity Community
Joining the cybersecurity community offers valuable insights. Networking enhances knowledge and skills. Here’s how to engage:
- Participate in online forums like Reddit or Stack Overflow.
- Attend local cybersecurity meetups.
- Follow industry leaders on social media.
Share experiences and learn from others. Collaboration boosts problem-solving skills. Consider contributing to open-source projects. This fosters teamwork and practical experience.
Credit: securityboulevard.com
Overcoming Challenges And Pitfalls
Penetration testing is vital for small businesses. It helps identify security weaknesses. However, many challenges can arise during this process. Understanding these challenges helps businesses overcome them effectively.
Dealing With Limited Resources
Small businesses often face resource constraints. This includes time, money, and personnel. Here are key strategies to manage limited resources:
- Prioritize Critical Assets: Focus on protecting essential data first.
- Use Automated Tools: Leverage software to streamline testing.
- Engage Third-Party Services: Consider hiring experts for specific tasks.
Small budgets can limit testing options. Choose cost-effective methods to ensure security. Consider these affordable approaches:
| Method | Cost | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Scanning | Low | Moderate |
| Internal Testing | Free | High |
| External Consultants | High | Very High |
Maintaining Operational Continuity
Penetration testing can disrupt daily operations. Planning reduces potential downtime. Follow these steps to maintain continuity:
- Schedule During Off-Hours: Conduct tests outside business hours.
- Notify Employees: Inform staff about testing dates.
- Establish a Recovery Plan: Prepare for unexpected disruptions.
Testing should not interfere with customer service. Ensure clients receive uninterrupted support. Here are tips to keep operations running smoothly:
- Limit Testing Scope: Focus on non-critical systems first.
- Use Staging Environments: Test in isolated settings before going live.
- Monitor Impact: Track performance during testing.
Case Studies: Small Business Penetration Test Scenarios
Understanding real-world examples helps small businesses grasp the importance of penetration testing. Case studies illustrate various scenarios. They show how businesses can strengthen their security. Let’s dive into two specific examples.
Retail Business Example
A local retail store wanted to protect customer data. They faced risks from online transactions and in-store systems. The store hired a penetration testing firm to evaluate their security.
The testing process included:
- Assessing the website for vulnerabilities.
- Testing the Point of Sale (POS) systems.
- Simulating phishing attacks on staff.
Results showed critical vulnerabilities:
| Finding | Severity | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection on website | High | Use prepared statements. |
| Weak passwords on POS | Medium | Implement strong password policies. |
| Phishing susceptibility | High | Conduct regular training sessions. |
After fixing these issues, the retail store improved its security. Customer trust increased, leading to higher sales.
Service Provider Scenario
A small IT service provider managed sensitive client data. They realized their systems needed a security check. A penetration test was essential to identify potential weaknesses.
The testing included:
- Network vulnerability scanning.
- Testing employee awareness of security threats.
- Assessing data protection policies.
Key findings included:
| Finding | Severity | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Unpatched software | High | Regularly update all software. |
| No two-factor authentication | Medium | Implement two-factor authentication. |
| Lack of data encryption | High | Encrypt sensitive client data. |
This service provider made necessary changes. They enhanced their data protection and improved client confidence.
Taking Action: Post-penetration Test Steps
After a penetration test, taking action is crucial. The insights gained help strengthen your security. Knowing what to do next can prevent future attacks. Implementing effective strategies is essential for small businesses.
Remediation Strategies
Identifying vulnerabilities is just the start. Remediation strategies help fix these issues. Focus on these key steps:
- Prioritize Vulnerabilities: Address the most critical ones first.
- Patch Software: Update systems and applications regularly.
- Improve Configurations: Change settings that may expose weaknesses.
- Conduct Training: Educate employees about security risks.
- Monitor Systems: Use tools to track unusual activities.
Consider using a vulnerability management tool. This tool helps automate patching and monitoring. Regular assessments help maintain security.
Building A Resilient Security Posture
A resilient security posture protects against future attacks. Here are effective ways to build it:
- Develop a Security Policy: Create guidelines for data protection.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Add extra layers of security.
- Regular Security Audits: Schedule audits to ensure compliance.
- Incident Response Plan: Prepare a plan for potential breaches.
- Engage Security Experts: Consult professionals for ongoing support.
Consider forming a security team. This team oversees all security measures. A proactive approach keeps your business safe.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Prioritize Vulnerabilities | Focus on critical issues first. |
| Patch Software | Keep systems and applications updated. |
| Employee Training | Educate staff on security best practices. |
Penetration Testing On A Budget
Small businesses often face tight budgets. Yet, they must ensure strong security. Penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities. You don’t need to spend a lot. Many affordable options exist.
Utilizing Free And Open-source Tools
Free tools can help detect security issues. Here are some popular options:
- Nmap – Scans networks for open ports.
- Metasploit – Automates finding vulnerabilities.
- OWASP ZAP – Tests web applications for security flaws.
These tools are powerful and user-friendly. They provide essential features without costs. Small businesses can save money while ensuring security.
Prioritizing Security Efforts
Focus on the most critical areas first. Identify high-risk assets. Here’s how to prioritize:
- Assess sensitive data locations.
- Evaluate network infrastructure.
- Review employee access levels.
Allocate resources wisely. Invest in training for staff. Regularly update software and systems. This approach maximizes security within budget constraints.
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Use free tools | Reduces costs |
| Train employees | Enhances awareness |
| Update software | Fixes vulnerabilities |
By utilizing these strategies, small businesses can effectively protect themselves. Strong security is possible without breaking the bank.
Future-proofing: Staying Ahead Of Threats
Small businesses face constant cybersecurity challenges. Keeping up with emerging threats is vital. Understanding penetration testing methodologies helps organizations stay secure. Future-proofing involves proactive measures and continuous improvement. This section covers essential strategies to stay ahead of threats.
Emerging Cybersecurity Trends
Cybersecurity evolves rapidly. Small businesses must watch for new trends. Here are key trends to consider:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI helps detect threats faster.
- Cloud Security: More businesses use cloud services.
- Remote Work Security: Protecting remote workers is crucial.
- Zero Trust Model: Verify every user before access.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay updated on laws and regulations.
Understanding these trends helps businesses adapt their security measures. Recognizing potential threats early can prevent costly breaches.
Continuous Monitoring And Improvement
Continuous monitoring is essential for effective cybersecurity. Regular assessments help identify vulnerabilities.
- Conduct Regular Penetration Tests: Schedule tests to find security gaps.
- Implement Real-time Monitoring Tools: Use software to track activities.
- Train Employees: Regular training reduces human error.
- Update Security Protocols: Adapt protocols to new threats.
- Review and Analyze Data: Regularly analyze security logs.
Establishing a culture of continuous improvement strengthens defenses. Small businesses must remain agile and responsive.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Penetration Testing For Small Businesses?
Penetration testing for small businesses is a security assessment. It simulates cyber attacks to identify vulnerabilities. This process helps businesses understand their security posture. By discovering weaknesses, companies can implement stronger defenses. Ultimately, it enhances overall cybersecurity and protects sensitive data.
Why Do Small Businesses Need Penetration Testing?
Small businesses need penetration testing to safeguard assets. Cyber threats are rising, targeting organizations of all sizes. Testing helps identify vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. Moreover, it ensures compliance with industry regulations. Regular assessments build customer trust and improve overall security.
How Often Should Small Businesses Conduct Penetration Tests?
Small businesses should conduct penetration tests annually or biannually. However, frequency may vary based on risk factors. New technologies or significant changes in the business warrant additional testing. Regular assessments ensure ongoing protection against evolving cyber threats. Consistency is key to maintaining robust security.
What Are Common Penetration Testing Methodologies?
Common penetration testing methodologies include OWASP, NIST, and PTES. Each framework provides guidelines for effective testing. OWASP focuses on web applications, while NIST covers broader security aspects. PTES emphasizes a structured approach to testing. Choosing the right methodology is crucial for comprehensive assessments.
Conclusion
Penetration testing is essential for small businesses to enhance their cybersecurity. Understanding various methodologies helps in choosing the right approach. Regular testing can identify vulnerabilities before attackers do. By investing in these practices, small businesses can protect sensitive data and build customer trust.
Stay proactive to ensure lasting security.



Leave a Reply