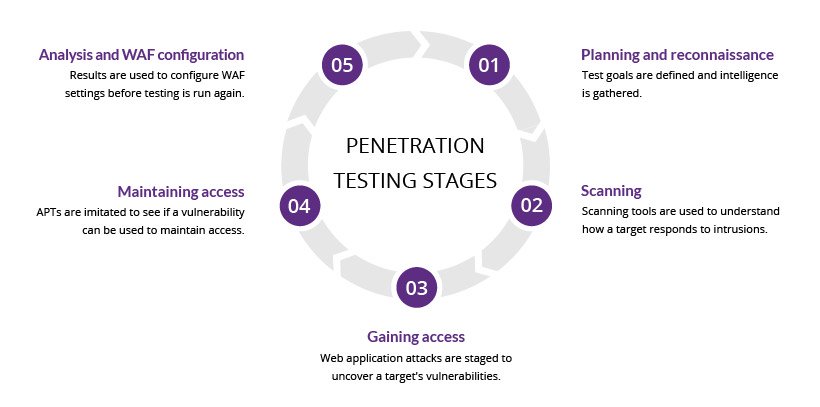
To conduct a web application penetration test, define the scope and gather relevant information about the application. Next, use automated tools and manual techniques to identify vulnerabilities.
How to Conduct a Web Application Penetration Test:Web application penetration testing is essential for identifying security weaknesses in online platforms. As cyber threats evolve, businesses must prioritize protecting sensitive data. A thorough penetration test simulates real-world attacks, highlighting vulnerabilities before malicious actors exploit them. This proactive approach helps organizations comply with regulations and build customer trust.
By regularly conducting these tests, companies can safeguard their digital assets and ensure robust security measures. Understanding how to carry out these assessments effectively can make a significant difference in an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. Investing in penetration testing is not just a technical necessity; it’s a critical business strategy.
Introduction To Web Application Penetration Testing
Web application penetration testing identifies security weaknesses in applications. This process simulates attacks to find vulnerabilities. It helps businesses protect sensitive data. Understanding this testing is crucial for any organization.
The Importance Of Security Testing
Security testing is vital for several reasons:
- Protects sensitive data: Safeguards user information and business assets.
- Boosts customer trust: Ensures clients feel safe using your services.
- Meets compliance requirements: Adheres to regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS.
- Prevents financial loss: Reduces the risk of costly data breaches.
Investing in security testing saves money in the long run. It helps avoid the expenses related to breaches.
Key Differences From Other Security Assessments
| Feature | Web App Penetration Testing | Other Security Assessments |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Application vulnerabilities | Network or system vulnerabilities |
| Method | Simulated attacks | Checklist-based evaluations |
| Depth | In-depth analysis | Overview assessments |
| Outcomes | Identifies specific vulnerabilities | General security posture |
Understanding these differences helps prioritize security efforts. Web application penetration testing offers a focused approach. It provides insights that other assessments may overlook.
Preparation For Penetration Testing
Preparation is key to a successful penetration test. Proper planning helps identify vulnerabilities in a web application. It sets the stage for effective testing and reporting.
Setting Clear Goals
Define what you want to achieve with the penetration test. Clear goals help focus the testing effort. Consider these points:
- Identify critical assets.
- Determine potential threats.
- Assess compliance requirements.
- Understand user access levels.
Establishing these goals will guide the entire testing process. Ensure all stakeholders agree on these objectives.
Legal Considerations And Permissions
Legal aspects are crucial in penetration testing. Always obtain written permission from the application owner. This ensures compliance with laws and regulations.
Consider the following:
- Document the scope of the test.
- Define the testing timeframe.
- Clarify liability agreements.
Ignoring legal aspects can lead to severe consequences. Always prioritize legal permissions before starting any test.
Selecting The Right Tools
Choosing the correct tools is vital for effective testing. The right tools help identify vulnerabilities accurately. Here are some popular tools:
| Tool Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Burp Suite | Web application security testing |
| Nessus | Vulnerability scanning |
| OWASP ZAP | Automated security testing |
| Metasploit | Exploitation framework |
Evaluate tools based on your goals. Test the tools in a controlled environment first. This ensures they meet your needs.
Understanding The Target Application
Before starting a web application penetration test, it’s vital to understand the target application. This involves analyzing its structure, functionality, and potential vulnerabilities. A thorough understanding helps identify risks and develop effective testing strategies.
Mapping The Application’s Architecture
Mapping the application’s architecture reveals how components interact. This step is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities. Here’s how to do it:
- Identify all components: List all modules and services.
- Understand data flow: Know how data moves through the application.
- Review documentation: Use existing architecture diagrams and documents.
- Use tools: Tools like OWASP ZAP can help visualize the architecture.
Creating a diagram can clarify the application’s structure. Use tools like Lucidchart or draw.io for visual representation. This diagram should include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Frontend | User interface and client-side interactions. |
| Backend | Server-side logic and database interactions. |
| API | Endpoints for communication between frontend and backend. |
Identifying Entry Points And User Roles
Knowing the entry points helps focus the test. Entry points are where users interact with the application. Here are steps to identify them:
- List user roles: Identify different user types in the application.
- Document entry points: Note where users log in, register, or access features.
- Analyze permissions: Understand what each user role can access.
Entry points may include:
- Login pages
- Forms for data submission
- API endpoints
Each entry point should be tested for vulnerabilities like:
- SQL Injection
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Authentication flaws
A clear understanding of user roles and entry points enhances testing effectiveness.

Credit: qualysec.com
Reconnaissance: Gathering Intelligence
Reconnaissance is the first step in a web application penetration test. It involves collecting information about the target. This knowledge helps identify potential vulnerabilities. Two primary methods exist: passive information collection and active information gathering.
Passive Information Collection
Passive information collection involves gathering data without direct interaction. This method keeps you under the radar. Here are some effective techniques:
- Search Engines: Use Google to find information about the target.
- Social Media: Explore social media platforms for user details.
- WHOIS Lookup: Get domain registration information.
- Public Records: Review public databases and reports.
These techniques can reveal useful insights. They may include:
| Data Type | Source |
|---|---|
| Domain Information | WHOIS |
| Email Addresses | Social Media |
| Server Details | Search Engines |
Active Information Gathering
Active information gathering involves direct interaction with the target. This method can be risky but provides deeper insights. Common techniques include:
- Port Scanning: Identify open ports and services.
- Service Enumeration: Discover versions of running services.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Check for known vulnerabilities.
These actions help map the application’s structure. They also expose potential entry points. Always use caution. Unchecked actions may trigger alarms.
Threat Modeling And Risk Assessment
Threat modeling and risk assessment are vital in a web application penetration test. These steps help identify potential security threats and assess risks. Understanding these elements allows teams to prioritize their efforts effectively. This process ensures the web application remains secure from attacks.
Identifying Potential Threats
Identifying potential threats involves examining various factors. Consider the following aspects:
- Attack Vectors: How can attackers access the application?
- Data Sensitivity: What type of data does the application handle?
- User Roles: What roles do users have? Are they exposed?
- External Dependencies: Does the application rely on third-party services?
Use a table to summarize common threats:
| Threat Type | Description |
|---|---|
| SQL Injection | Attacker manipulates SQL queries to access data. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Malicious scripts run in user browsers. |
| Denial of Service (DoS) | Overwhelms the application, causing outages. |
| Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) | Attacker tricks users into unwanted actions. |
Prioritizing Vulnerabilities
After identifying threats, prioritize vulnerabilities based on their potential impact. Use a risk assessment matrix for clarity. Consider the following criteria:
- Likelihood: How probable is the attack?
- Impact: What is the potential damage?
- Exposure: How accessible is the vulnerability?
Here’s a simple risk assessment matrix:
| Likelihood | Impact | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| High | High | Critical |
| Medium | High | High |
| Low | High | Medium |
| High | Low | Medium |
By prioritizing vulnerabilities, teams can focus on fixing the most critical issues first. This systematic approach improves the overall security posture of the web application.
Vulnerability Discovery
Vulnerability discovery is a key phase in a web application penetration test. It identifies security weaknesses in an application. These weaknesses can lead to data breaches or system compromises. Understanding vulnerabilities helps improve web application security.
Common Web Application Vulnerabilities
Knowing common vulnerabilities is essential for effective testing. Here are some frequent issues found in web applications:
| Vulnerability | Description |
|---|---|
| SQL Injection | Attacker manipulates SQL queries to access data. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Malicious scripts run in a user’s browser. |
| Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) | Tricks a user into executing unwanted actions. |
| Insecure Direct Object References | Unauthorized access to objects via modified requests. |
| Security Misconfiguration | Improper configuration leads to security gaps. |
Automated Scanning Vs. Manual Testing
Both automated scanning and manual testing have unique advantages. Understanding these can enhance your testing strategy.
- Automated Scanning:
- Fast and efficient.
- Identifies many common vulnerabilities.
- Requires less human effort.
- Manual Testing:
- More thorough and nuanced.
- Can identify complex vulnerabilities.
- Requires skilled security professionals.
Using both methods often yields the best results. Automated tools find basic issues. Manual testing uncovers hidden vulnerabilities.
Exploitation Techniques
Exploitation techniques are crucial in a web application penetration test. They help security experts use identified vulnerabilities. This section covers two main aspects: crafting exploits and maintaining access.
Crafting Exploits For Identified Vulnerabilities
After finding vulnerabilities, the next step is crafting exploits. Exploits are tools or methods that take advantage of weaknesses. Here are key techniques:
- SQL Injection: Manipulate database queries through user input.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Inject malicious scripts into web pages.
- Command Injection: Execute system commands via input fields.
Each exploit requires careful crafting:
- Identify the vulnerability.
- Understand the application behavior.
- Develop the exploit code.
- Test the exploit in a safe environment.
| Vulnerability Type | Common Exploit |
|---|---|
| SQL Injection | ‘ OR ‘1’=’1 |
| XSS | |
| Command Injection | ; ls -la |
Maintaining Access And Pivoting
Once access is gained, maintaining that access is vital. It allows continued testing and exploration of the application. Techniques for maintaining access include:
- Backdoors: Install hidden entry points for future access.
- Web Shells: Upload scripts that allow control over the server.
- Credential Harvesting: Gather user credentials for further exploitation.
Pivoting is key for deeper exploration. It involves moving from one system to another. This expands the range of vulnerabilities you can exploit. Follow these steps:
- Identify network connections.
- Access other systems using captured credentials.
- Test additional applications for vulnerabilities.
Both maintaining access and pivoting enhance the penetration testing process. They provide a comprehensive view of security weaknesses.

Credit: blog.securelayer7.net
Post-exploitation And Analysis
After successful exploitation, focus shifts to analyzing the impact. This phase uncovers vulnerabilities and assesses risks. Understanding findings helps in strengthening security measures.
Assessing The Impact
Assessing the impact of the exploitation is crucial. It helps in understanding potential damage. Key areas to analyze include:
- Data Breach: Identify sensitive data exposed.
- System Integrity: Check for unauthorized changes.
- Access Control: Review unauthorized user access.
Use a table to summarize findings:
| Vulnerability | Impact Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | High | Patch application and validate inputs. |
| Cross-Site Scripting | Medium | Sanitize user inputs. |
| Insecure Direct Object References | High | Implement proper access controls. |
Gathering Evidence And Logging
Documenting findings is essential for future reference. Collect evidence from the test. This includes:
- Logs: Capture server and application logs.
- Screenshots: Take screenshots of vulnerabilities.
- Exploit Details: Note methods and tools used.
Ensure logs are clear and organized. Use a consistent format for easy review. This approach aids in compliance and accountability.
Consider using a log management tool for better organization.
Reporting And Communication
Effective reporting and communication are key after a web application penetration test. Clear communication helps stakeholders understand vulnerabilities and risks. Proper documentation ensures everyone knows what to fix and how to improve security.
Documenting Findings
Documenting findings clearly is crucial. Use simple language and clear visuals. Include the following in your report:
- Executive Summary: A brief overview of findings.
- Scope: Outline the tested areas.
- Methodology: Explain how testing was conducted.
- Vulnerabilities: List all identified vulnerabilities.
- Risk Ratings: Assess the severity of each issue.
Use tables to summarize vulnerabilities:
| Vulnerability | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SQL Injection | High | Allows attackers to manipulate database queries. |
| XSS | Medium | Enables scripts to run in users’ browsers. |
| CSRF | Low | Tricks users into submitting unwanted actions. |
Providing Actionable Remediation Steps
Actionable remediation steps guide developers on fixing issues. Each vulnerability should have clear steps. Include:
- Identify: Locate the vulnerable code or configuration.
- Fix: Provide code snippets or configuration changes.
- Test: Suggest retesting methods to verify fixes.
For example:
// Example code snippet to fix SQL Injection
$db->prepare("SELECT FROM users WHERE id = :id");
$db->bindParam(':id', $userId);
$db->execute();
Clear remediation steps make it easy for teams to act quickly. This reduces risks and improves security posture.

Credit: kratikal.com
Remediation And Retesting
After conducting a web application penetration test, it’s crucial to address any vulnerabilities found. Remediation involves fixing these issues. Retesting ensures that the fixes work and no new problems have been introduced. This process protects your application from attacks.
Working With Development Teams
Effective remediation requires collaboration with development teams. Here are steps to engage them:
- Share detailed reports of vulnerabilities.
- Prioritize issues based on risk levels.
- Involve developers in planning fixes.
- Provide guidance on secure coding practices.
Collaboration fosters a security-focused culture. It helps developers understand the importance of security. This teamwork leads to faster and more effective solutions.
Verifying Fixes And Closing Gaps
Once developers implement fixes, retesting is vital. Follow these steps:
- Conduct a new penetration test on the updated application.
- Check if the vulnerabilities are resolved.
- Look for any new vulnerabilities that may have appeared.
- Document all findings and improvements.
Consider using automated tools for retesting. These tools can quickly identify issues. Manual testing may still be necessary for complex scenarios.
| Step | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Share Reports | Inform developers about vulnerabilities |
| 2 | Prioritize Issues | Focus on the most critical problems |
| 3 | Retest | Verify that fixes are effective |
| 4 | Document Findings | Maintain a record of security improvements |
Regular retesting keeps your application secure. It ensures no gaps remain. A proactive approach to security is essential for long-term protection.
Best Practices For Continuous Security
Ensuring continuous security in web applications is crucial. Implementing best practices keeps your application safe from threats. It protects user data and maintains trust. Below are key strategies for ongoing security.
Implementing A Secure Development Lifecycle
A Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL) enhances security from the start. Follow these steps to create an effective SDL:
- Planning: Define security requirements early.
- Design: Use secure design patterns. Avoid common vulnerabilities.
- Development: Train developers in secure coding practices.
- Testing: Conduct regular security testing throughout.
- Deployment: Secure the environment before going live.
- Maintenance: Monitor and update regularly.
Using an SDL helps catch issues early. It reduces risks and costs associated with security breaches.
Regular Testing And Updates
Regular testing is vital for maintaining security. Schedule frequent penetration tests to identify weaknesses. Follow these tips for effective testing:
- Perform tests after significant changes.
- Use automated tools for efficiency.
- Engage third-party experts for fresh insights.
Keep your software up to date. Apply patches and updates promptly. This reduces vulnerabilities.
Consider using a table for tracking updates:
| Software | Last Updated | Next Update Due |
|---|---|---|
| Web Server | 2023-09-01 | 2023-12-01 |
| Framework | 2023-08-15 | 2023-11-15 |
| Database | 2023-10-01 | 2024-01-01 |
Regular testing and timely updates form a strong defense. Stay proactive in securing your web applications.
Ethical And Legal Considerations
Conducting a web application penetration test requires careful attention to ethics and legality. Understanding these aspects ensures that tests are performed responsibly. It also protects both the tester and the organization being tested.
Staying Within Legal Boundaries
Legal boundaries are crucial in penetration testing. Always obtain explicit permission before testing. Unauthorized access can lead to severe legal consequences.
- Get a signed agreement from the client.
- Define the scope of testing clearly.
- Respect privacy laws and regulations.
Consider these key legal documents:
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| Authorization Letter | Granting permission for testing activities. |
| Non-Disclosure Agreement | Protecting confidential information shared during testing. |
| Scope Document | Defining what areas will be tested. |
Ethical Disclosure Of Vulnerabilities
Ethics play a vital role in penetration testing. If vulnerabilities are discovered, handle them responsibly. Immediate disclosure to the client is essential.
- Document all findings thoroughly.
- Provide clear recommendations for remediation.
- Follow a timeline for reporting issues.
Keep these principles in mind:
- Act in the best interest of the client.
- Maintain confidentiality of sensitive data.
- Ensure full transparency throughout the process.
Respecting ethical guidelines builds trust. It enhances the reputation of the testing professional.
Conclusion: Enhancing Web Security
Conducting a web application penetration test is vital. It helps identify weaknesses. Fixing these issues enhances your site’s security. Let’s summarize key takeaways and explore the future of penetration testing.
Summary Of Key Takeaways
- Understand Vulnerabilities: Learn about common security flaws.
- Use Tools: Employ reliable tools for testing.
- Document Findings: Keep detailed records of issues.
- Fix Issues: Prioritize and resolve identified problems.
- Regular Testing: Schedule tests frequently for ongoing security.
The Future Of Penetration Testing
Penetration testing is evolving rapidly. Here are key trends:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation | More tools will automate testing processes. |
| AI Integration | Artificial intelligence will enhance threat detection. |
| Cloud Security | Focus on securing cloud applications will increase. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Stricter rules will shape testing practices. |
Staying informed is crucial. Embrace new techniques and tools. This proactive approach boosts web security.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Web Application Penetration Testing?
Web application penetration testing is a simulated cyber attack. It identifies vulnerabilities in web applications. The process evaluates the security posture by exploiting weaknesses. This helps organizations safeguard sensitive data and enhance their overall security measures.
Why Is Penetration Testing Important For Web Apps?
Penetration testing is crucial for web apps to identify vulnerabilities. It helps organizations understand their security risks. Regular testing can prevent data breaches and attacks. By addressing weaknesses, companies can protect user data and maintain trust.
How Often Should Penetration Tests Be Conducted?
Organizations should conduct penetration tests at least annually. However, testing should also occur after significant changes. This includes updates, new features, or architecture modifications. Frequent assessments ensure continuous security and help mitigate emerging threats.
What Tools Are Used In Penetration Testing?
Common tools for penetration testing include Burp Suite, OWASP ZAP, and Metasploit. These tools help identify vulnerabilities in web applications. They automate various testing processes, making assessments more efficient. Each tool offers unique features tailored for specific testing needs.
Conclusion
Conducting a web application penetration test is essential for safeguarding your digital assets. It helps identify vulnerabilities and strengthens your security posture. Regular testing not only protects sensitive data but also builds trust with users. Stay proactive and make penetration testing a key part of your security strategy for lasting protection.



Leave a Reply